NVMe/TCP vs NVMe/RoCE: Which Protocol For High-Performance Storage?
Dec 10th, 2025 | 11 min read
Table Of Contents
- What Is NVMe/TCP?
- What Is NVMe/RoCE (RDMA)?
- NVMe/TCP vs NVMe/RoCE: A Comparison of Trade-Offs
- Use Cases: Where Each Protocol Shines
- Investment Considerations: RDMA Might Already Be in Your Infrastructure
- Why Simplyblock Supports Both NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RoCE
- Real-World Example: Mixed-Protocol Kubernetes Deployment
- A Smarter Investment Path: Start Simple, Scale Fast
- Conclusion: Freedom, Flexibility, and Performance Without Compromise
- FAQs
As modern workloads become faster, smarter, and more distributed, the infrastructure behind them must keep up. Enterprise applications, especially those driven by AI, analytics, and cloud-native platforms, demand ultra-fast low-latency data access. At the heart of this performance revolution is NVMe, a protocol that unlocks the true potential of flash storage.
But NVMe itself comes in multiple forms. Two of the most prominent are NVMe over TCP (NVMe/TCP) and NVMe over RoCE (RDMA). Choosing between them can be a pivotal decision. One that impacts latency, scalability, and cost. At simplyblock, we support both. Why? Because no two environments are the same.
Let’s explore what makes these two protocols different, when to use each, and how simplyblock gives you the flexibility to run both in a single software-defined storage platform.
What Is NVMe/TCP?
NVMe/TCP: Accessible, Scalable, and Cloud-Native Ready
NVMe over TCP extends NVMe performance across standard Ethernet networks using the well-known TCP/IP stack. This makes it incredibly easy to deploy and ideal for environments that prioritize flexibility and scalability. Since NVMe/TCP doesn’t require specialized hardware or complex configuration, it fits naturally into today’s hybrid and multi-cloud setups.
In practical terms, NVMe/TCP works on nearly any existing data center hardware. It doesn’t need RDMA-capable network interface cards or switch-level tuning. That means organizations can adopt it without changing their infrastructure, keeping capital investment low while still modernizing their storage interface.
This protocol has become especially popular in Kubernetes storage environments, where agility and compatibility matter more than ultra-low latency. DevOps teams love how easily it integrates with container orchestration systems, CI/CD pipelines, and microservices architecture. You get decent performance, rapid deployment, and operational simplicity.
But it’s not without trade-offs.
Because it relies on the TCP/IP stack, NVMe/TCP introduces slightly more latency and CPU overhead compared to RDMA. In typical configurations using simplyblock with NVMe/TCP, you might see storage latencies between 300 and 500 microseconds. While this is still much faster than traditional iSCSI or SATA-based storage, it may not be enough for real-time workloads that require consistent sub-millisecond response times.
What Is NVMe/RoCE (RDMA)?
NVMe/RoCE: The Protocol for Performance-Critical Applications
NVMe over RoCE, or NVMe/RDMA over Converged Ethernet, is all about performance. It uses Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) to bypass the traditional network stack, enabling direct memory-to-memory data transfer between systems. This removes most of the latency and CPU involvement typically found in storage access operations.
Real-world deployments using NVMe/RoCE often see latencies drop to 100–150 microseconds, providing also much more consistent tail latency (or p99 latency). That makes a significant difference in environments where timing precision is everything. Think high-frequency trading platforms, real-time data analytics, or AI model training and inference.
But there’s a cost. NVMe/RoCE requires RDMA-capable NICs and ideally a lossless Ethernet fabric. These conditions demand careful network configuration and switch tuning. It’s not a plug-and-play setup. However, once optimized, the results can be transformational for compute-intensive workloads that depend on consistent, high-throughput, low-latency storage.
NVMe/TCP vs NVMe/RoCE: A Comparison of Trade-Offs
Both protocols unlock NVMe’s speed advantage, but they serve different priorities.
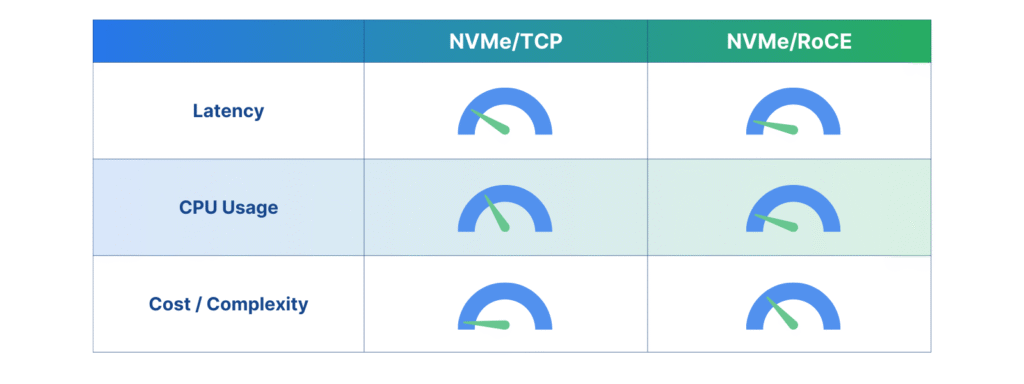
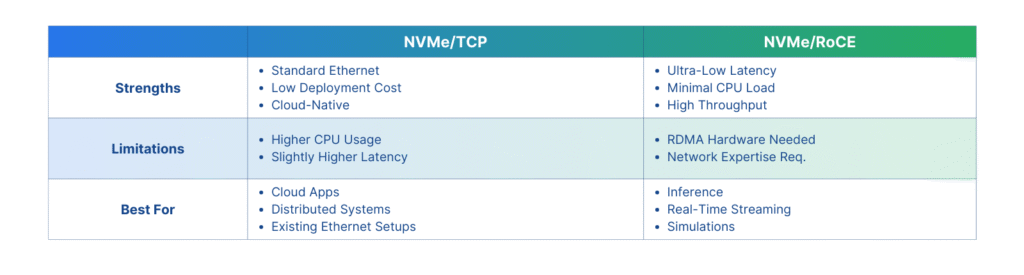
NVMe/TCP offers broad compatibility and low-cost deployment. It fits best in distributed systems, cloud-native applications, and environments that already rely on standard Ethernet infrastructure. Its higher CPU usage and slightly elevated latency make it less ideal for tasks where timing precision is essential.
NVMe/RoCE excels in performance, offering the lowest latency and minimal CPU load. But it requires investment in RDMA-capable hardware and demands more from your network team. If your workloads involve large-scale inference, real-time data streaming, or scientific simulations, NVMe/RoCE is worth the complexity.
This isn’t a matter of which protocol is better. It’s about which is better for your use case.
Use Cases: Where Each Protocol Shines
NVMe/TCP in Kubernetes and Distributed Workloads
Kubernetes environments thrive on flexibility. When applications are containerized and orchestrated across many nodes, storage needs to be fast but also easy to manage. NVMe/TCP is the perfect match here. It supports disaggregated storage, integrates smoothly with service meshes and operators, and scales horizontally with minimal friction.
Imagine a company running SaaS applications built on microservices. Each container reads from and writes to persistent volumes provided by a shared storage backend. NVMe/TCP allows this backend to deliver strong performance over existing Ethernet, without requiring specialized NICs or changes to network topology.
In this scenario, teams can focus on deploying features and maintaining uptime and not managing storage complexity.
NVMe/RoCE in AI, ML, and Financial Systems
On the other hand, performance-critical workloads demand more. A trading platform executing thousands of orders per second can’t afford jitter. An AI pipeline feeding GPU accelerators with massive datasets can’t tolerate slow reads.
In these environments, NVMe/RoCE delivers. It provides near-direct-attached-storage latency while scaling across the network. A media analytics company using machine learning to process video feeds in real time, for example, benefits from the protocol’s ability to move data with minimal CPU overhead and maximum speed.
It’s in these use cases, where raw performance is not optional, that NVMe/RoCE justifies its complexity.
Investment Considerations: RDMA Might Already Be in Your Infrastructure
One common concern when evaluating NVMe/RoCE is the perceived cost of upgrading to RDMA-capable networking. But in reality, many modern data center NICs already support RDMA out of the box. Popular models like the NVIDIA ConnectX-5 and ConnectX-6, Intel E810, or Broadcom NetXtreme-E series offer full RoCE support and are widely used in enterprise deployments. If your servers are equipped with any of these, you may already have the required hardware. It often comes down to enabling RoCE features in the firmware and tuning your switches (not replacing physical components).
Let’s take a practical investment example. Upgrading a standard server to support NVMe/RoCE may only require a firmware update or minor configuration on a ConnectX-5 100GbE NIC, which already supports both RoCE v1 and v2. On the switch side, data center-class switches from vendors like Arista, Juniper, or NVIDIA/Mellanox often ship with lossless Ethernet and DCB (Data Center Bridging) capabilities built in. With a modest investment in tuning and validation, many organizations can enable NVMe/RoCE using existing networking gear.
This makes the transition far more accessible than expected. Start with NVMe/TCP where ease of deployment matters, and selectively turn on RDMA where your workloads demand peak performance. There’s no need to redesign your stack. Just enable what’s already there. Furthermore, with simplyblock you can mix both protocols in a single cluster for greatest flexibility and lowest “barrier to entry” for using RDMA.
Why Simplyblock Supports Both NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RoCE
At simplyblock, we believe in removing trade-offs, not creating them. Our software-defined block storage platform is protocol-agnostic by design. That means we support NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RoCE natively, without requiring customers to commit to one or the other.
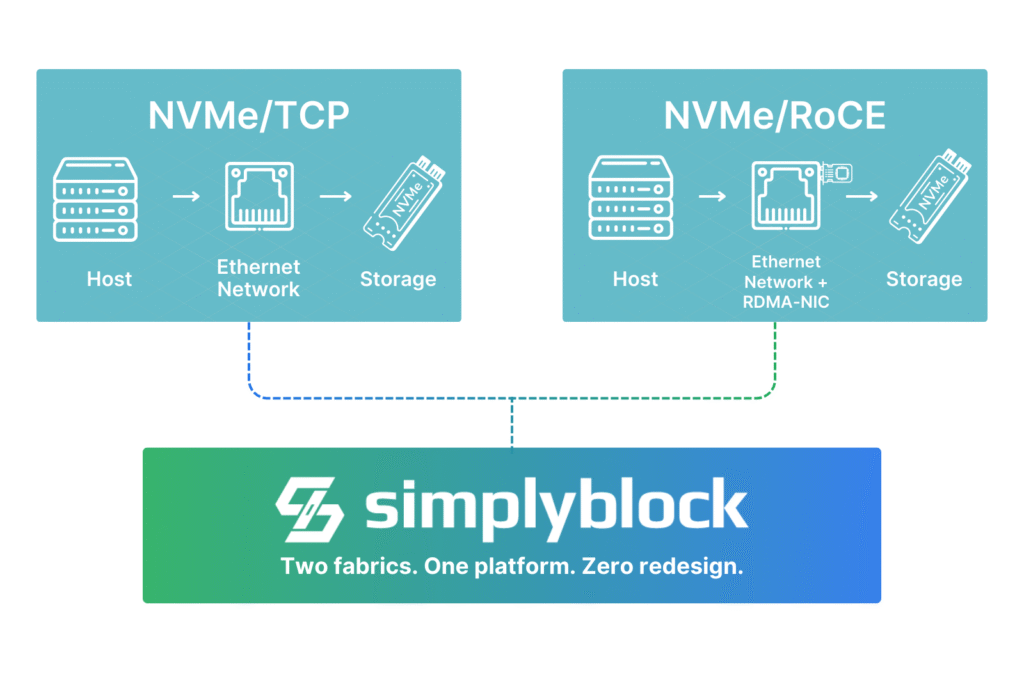
This gives you complete control over how storage interacts with your workloads. In one Kubernetes cluster, you might run general-purpose workloads over NVMe/TCP, while assigning RDMA-enabled nodes to high-performance GPU tasks that use NVMe/RoCE. Both can access the same storage pool, using the same software layer.
Our platform auto-detects the network and hardware capabilities during deployment and optimizes performance accordingly. We even benchmark the nodes in real-time to create quality of service baselines. This means your applications get consistent performance regardless of which protocol they use.
You’re not locked into a vendor-specific appliance, and you don’t need to redesign your infrastructure to support both. Simplyblock runs wherever you need it to – on-premises, across clouds, or at the edge. With or without specialized hardware.
Real-World Example: Mixed-Protocol Kubernetes Deployment
Consider a tech startup running multiple AI services in Kubernetes. They deploy a cluster with two node pools. One is composed of standard VMs running typical business logic, dashboards, and user services. The second pool features RDMA-capable bare-metal nodes with GPU acceleration for ML training.
Both node pools access shared volumes managed by Simplyblock. The standard pool uses NVMe/TCP. The AI nodes, needing faster read/write access to training datasets, use NVMe/RoCE. All of this runs on a unified backend, using the same software-defined storage layer.
No data is duplicated. No services are siloed. Simplyblock routes IO efficiently, applies performance policies, and gives every workload the protocol it needs.
This architecture makes it easy to scale, test, and optimize without worrying about the limits of your storage stack.
A Smarter Investment Path: Start Simple, Scale Fast
Supporting both protocols also makes financial sense. You can start with NVMe/TCP using existing infrastructure. This lowers your initial capital expenditure while still giving you strong NVMe-level performance.
As certain workloads evolve, such as AI or real-time processing, you can selectively introduce RDMA hardware and enable NVMe/RoCE. No forklift upgrades. No vendor lock-ins. Just a smooth path from flexibility to performance.
Because simplyblock is hardware-agnostic and built on open standards like NVMe-oF, you can grow your architecture on your terms. That includes hyperconverged setups, disaggregated storage, or hybrid cloud environments. The storage layer remains consistent, even as the protocol and hardware mix changes over time. Learn more about our MAUS architecture.
Conclusion: Freedom, Flexibility, and Performance Without Compromise
Choosing between NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RoCE isn’t about picking sides. It’s about enabling the right storage behavior for the right workload. In a world where performance, scalability, and cost all matter, a one-size-fits-all approach no longer works.
With simplyblock, you don’t have to compromise. Our support for both NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RoCE means you can optimize for today while preparing for tomorrow. Whether you’re scaling Kubernetes clusters, running AI pipelines, or supporting latency-sensitive enterprise applications, our platform gives you the control and performance you need.
Experience storage that adapts to your strategy. Not the other way around.
FAQs
Yes, NVMe/RoCE typically delivers lower latency—often between 100 and 150 microseconds—compared to NVMe/TCP, which usually ranges from 300 to 500 microseconds. However, the difference is most noticeable in latency-critical workloads such as AI inference or financial trading.
Absolutely. Simplyblock supports both protocols within a single software-defined storage platform. This means you can run general workloads over NVMe/TCP and assign high-performance tasks to NVMe/RoCE nodes without changing your storage backend.
In many cases, no. If your infrastructure uses NICs such as ConnectX‑5 or newer, Intel E810, or equivalent enterprise Ethernet adapters, RoCE support is likely already present. Enabling NVMe/RoCE may only require firmware updates, driver configuration, and proper network tuning rather than new hardware purchases.
Many modern data center NICs already support RoCE and RDMA. Common examples include the NVIDIA Mellanox ConnectX‑5, ConnectX‑6, and ConnectX‑7 series, Intel Ethernet E810 adapters, and Broadcom NetXtreme‑E NICs. These NICs are widely deployed in enterprise and cloud environments and often ship with RDMA capabilities enabled or ready to be enabled via firmware.
NVMe/TCP is generally better for Kubernetes due to its flexibility, ease of deployment, and compatibility with standard networking. However, if certain pods or workloads require extremely low latency, NVMe/RoCE can be used for those specific nodes or services.
Yes. Simplyblock is fully standards-based and supports NVMe-oF, including both NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RDMA protocols. This ensures compatibility across environments without the need for proprietary host-side drivers.
Yes. With Simplyblock, you can start with NVMe/TCP and migrate selected workloads to NVMe/RoCE as needed. There’s no need to re-architect your storage; both protocols are supported simultaneously and auto-detected during deployment.