NVMe over FC
Terms related to simplyblock
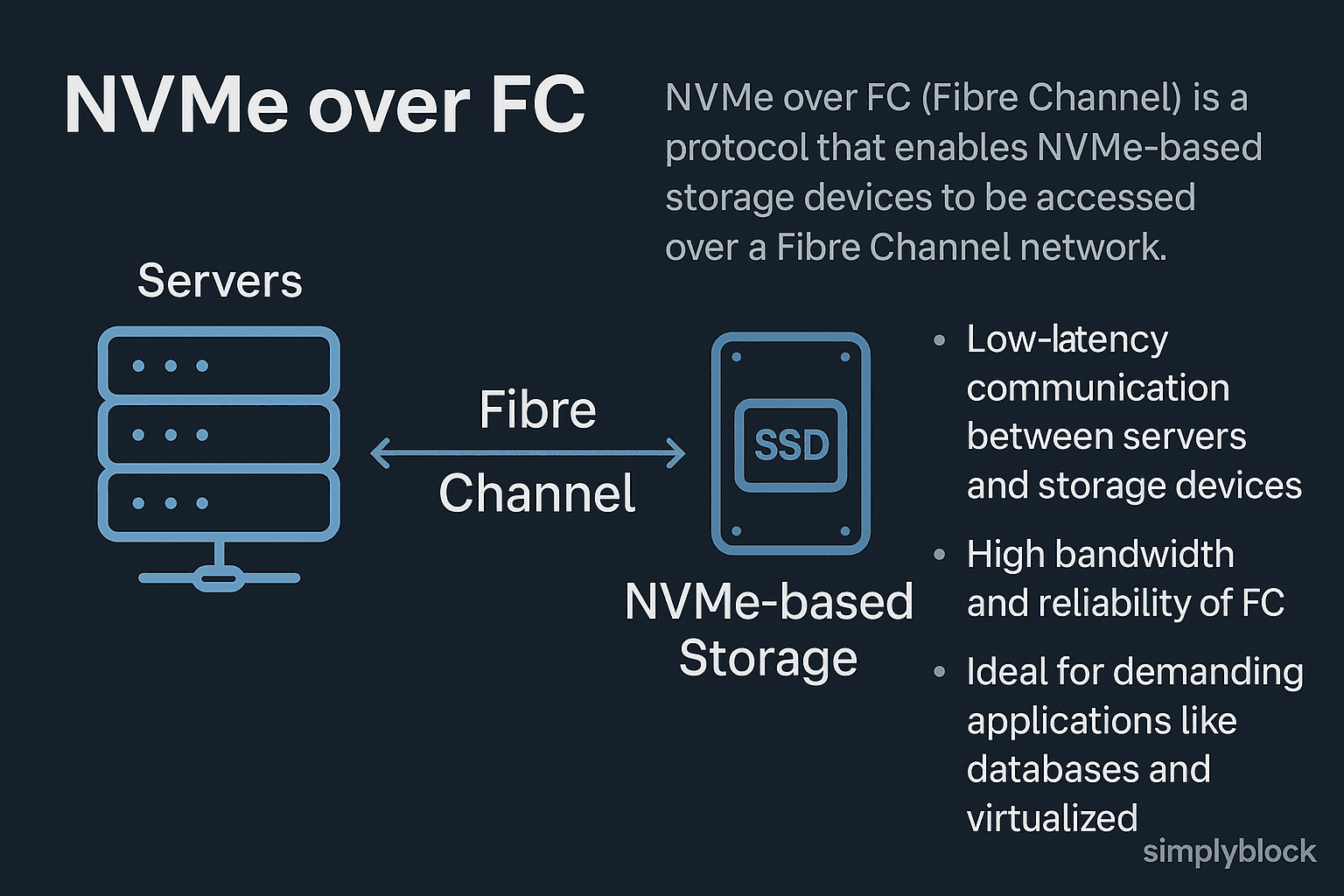
NVMe over FC (Fibre Channel), or NVMe/FC, is a storage protocol that enables NVMe command sets to run natively over Fibre Channel fabrics. This implementation combines the performance advantages of NVMe storage with the deterministic, lossless characteristics of FC-based infrastructure. It is a key transport protocol within the NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) specification.
Enterprises that have standardized on SAN infrastructure built around Fibre Channel can use NVMe/FC to reduce latency and increase throughput without replacing existing hardware. Unlike traditional SCSI-based FCP, NVMe/FC removes legacy command translation layers, resulting in reduced overhead and superior performance for flash-optimized storage environments.
How NVMe over FC Works
NVMe over FC operates by encapsulating NVMe commands directly into FC frames. This allows storage targets and initiators to communicate across Fibre Channel switches using the same physical infrastructure as traditional FC SANs. Vendors implement NVMe/FC using standard FC host bus adapters (HBAs) and firmware updates, without needing changes to FC switches.
As both NVMe and FC support multi-queueing and high parallelism, combining the two enables faster, more efficient storage access for applications with demanding I/O profiles, such as databases, virtualization platforms, and AI/ML workloads.
Benefits of NVMe over FC
Organizations benefit from NVMe/FC when they need to modernize performance without dismantling their FC-based infrastructure. Key benefits include:
- Sub-millisecond latency due to an efficient protocol stack and high-speed FC fabric.
- High throughput leveraging native NVMe parallelism and FC bandwidth (16G, 32G, and 64G).
- Reduced CPU overhead as NVMe bypasses the SCSI translation layer.
- Minimal disruption to existing SAN architecture and zoning practices.
- Improved scalability with support for more namespaces and queues.
This makes NVMe/FC a strong choice for performance-sensitive workloads that are already operating in FC-centric environments.
NVMe/FC Compared to Other Transports
Enterprises evaluating NVMe over Fabrics options should consider how NVMe/FC stacks up against Ethernet-based alternatives like NVMe over TCP and NVMe over RDMA. NVMe/FC requires FC infrastructure, while NVMe/TCP operates on commodity Ethernet and is better suited to cloud-native environments.
| Feature | NVMe over FC | NVMe over TCP | NVMe over RDMA (RoCE/iWARP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport Medium | Fibre Channel | Standard Ethernet (TCP/IP) | Ethernet with RDMA NICs |
| Hardware Requirements | FC HBAs, FC switches | Standard NICs | Specialized NICs |
| Latency | Very low (100µs–300µs) | Low (200–400µs) | Very low (<100µs) |
| Management Complexity | Moderate | Low | High |
| Legacy Integration | Seamless with existing SAN | Best for new deployments | Requires RDMA support |
| Cost Efficiency | Best when FC is in place | High on commodity hardware | High performance, high cost |
Enterprise Use Cases for NVMe over FC
Enterprises adopting NVMe/FC typically run high-performance, latency-sensitive workloads on well-established FC networks. Common use cases include:
- Enterprise databases (PostgreSQL, Oracle, SAP HANA) running on flash arrays.
- High-density virtualization platforms such as VMware or Hyper-V.
- Tier-1 SAN environments are transitioning from SCSI-based FCP to NVMe command sets.
- Private clouds require consistent latency and lossless packet delivery.
- Regulated industries (e.g., financial, healthcare) with existing FC infrastructure and strict performance SLAs.
For organizations using Kubernetes or hybrid storage environments, NVMe over TCP offers a more flexible alternative, which is the basis of simplyblock’s architecture.
NVMe over FC and Simplyblock™
At simplyblock, the architectural focus lies on NVMe over TCP to deliver high-performance distributed storage on Ethernet without specialized hardware. By bypassing the FC layer and utilizing standard IP networking, simplyblock enables scalable block storage with sub-millisecond latency and high IOPS per CPU core, especially in Kubernetes, cloud-native, and hybrid environments.
With a foundation in software-defined storage, simplyblock provides features like advanced erasure coding, multi-tenancy with QoS, and CSI integration for Kubernetes.
Related Terms
Teams often review these glossary pages alongside NVMe over FC when upgrading existing Fibre Channel SANs to NVMe semantics, validating discovery workflows, and ensuring predictable pathing for Kubernetes Storage and Software-defined Block Storage. This includes comparisons with NVMe/TCP, where Ethernet standardization is a priority.
External Resources
For further reading and technical specifications on NVMe over FC, consider the following resources:
- NVM Express over Fabrics Specification
- Fibre Channel Overview – Wikipedia
- NVM Express (NVMe) – Wikipedia
- What is NVMe over FC? – TechTarget
- NVMe over Fibre Channel – Broadcom
Questions and Answers
NVMe over Fibre Channel (NVMe/FC) is ideal for enterprises needing ultra-low latency and high IOPS on existing SAN infrastructure. It combines the speed of NVMe with the reliability of Fibre Channel, making it well-suited for databases, virtualization, and large-scale transactional systems.
While NVMe/FC provides excellent performance on legacy SAN infrastructure, NVMe over TCP offers similar benefits over standard Ethernet. NVMe/TCP is more flexible and cost-effective for modern, cloud-native deployments without requiring proprietary Fibre Channel hardware.
NVMe/FC can be used in Kubernetes, but it typically requires specialized hardware and is less cloud-native. For simpler integration and scalability, Kubernetes-native NVMe storage using TCP is preferred for containerized, dynamic environments.
Encryption is not built into the NVMe/FC protocol itself—it depends on the storage backend. For secure, multi-tenant environments, it’s best to implement encryption-at-rest at the storage volume level with isolated keys per tenant or volume.
NVMe/FC delivers high performance but relies on costly Fibre Channel infrastructure. It lacks the openness and scalability of NVMe/TCP and is harder to deploy in hybrid cloud or DevOps environments, where software-defined storage is more adaptable.
