Tail Latency
Terms related to simplyblock
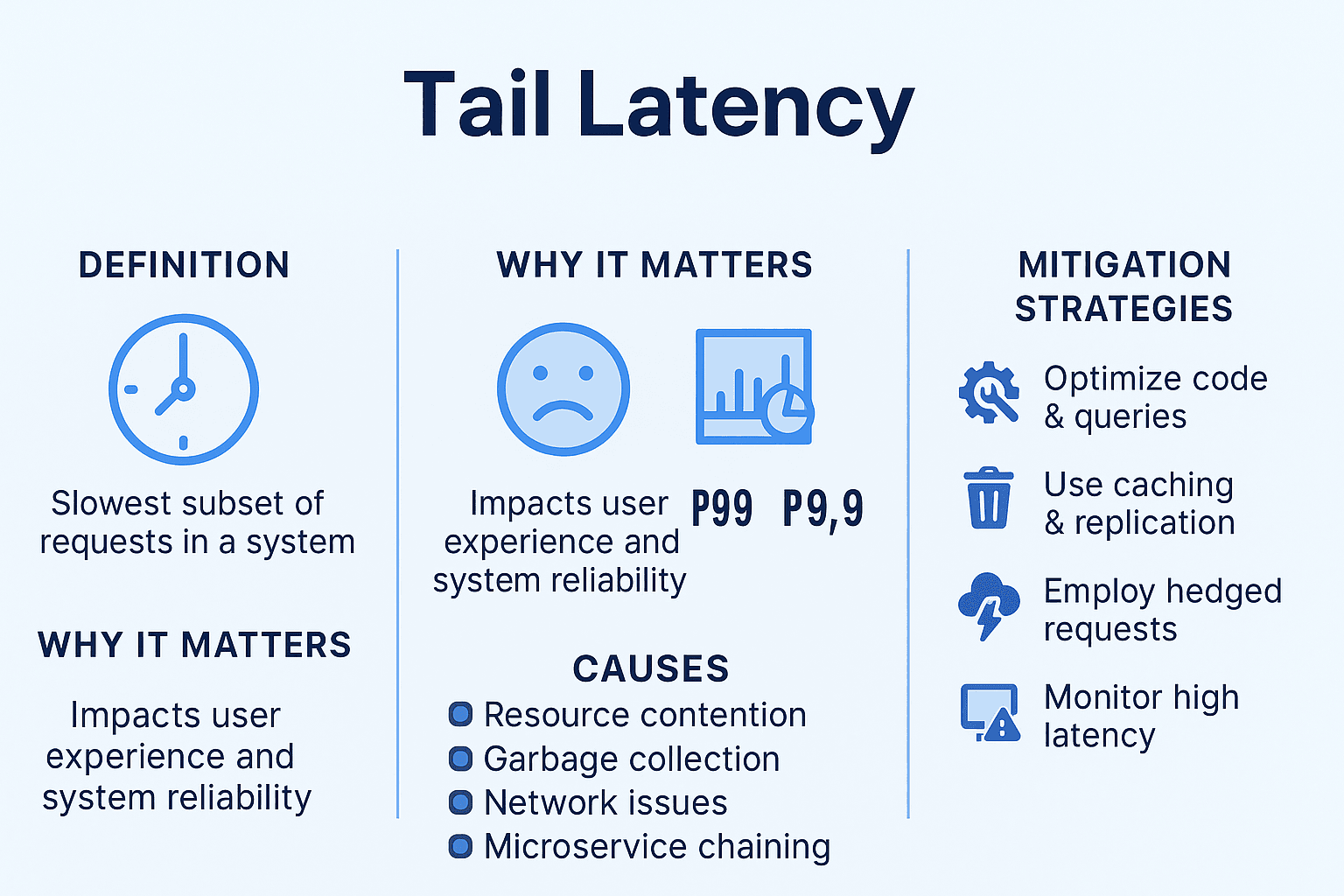
Tail latency refers to the slowest requests in a system, often representing the “outliers” in latency distribution. While most requests are processed within a reasonable time frame, tail latency highlights the few requests that take significantly longer. This can have a serious impact on the performance of high-demand, real-time applications, making it critical to address and optimize.
Tail latency affects system performance, and replication can help minimize it to ensure fast, reliable services for your users.
What Causes Tail Latency?
Tail latency occurs when certain requests or transactions experience higher latency than the average, causing delays in system response times. These delays can be caused by various factors, including:
- Network congestion: Slow or fluctuating network conditions can delay data transmission, contributing to tail latency.
- Server overload: High traffic or insufficient server resources can lead to delayed processing of certain requests.
- Replication lag: When data replication across multiple nodes or regions isn’t synchronized properly, requests may be delayed until data becomes available.
Even if the average latency is low, a few slow requests—referred to as tail latency—can significantly degrade the user experience.
🚀 Optimize Tail Latency with Simplyblock’s Real-Time Data Replication
Minimize delays and ensure faster data access across your infrastructure.
👉 Improve Performance and Reduce Tail Latency with Simplyblock →
Why is Tail Latency Important?
For modern applications, especially those running on cloud infrastructure, managing tail latency is critical. While most transactions may be fast, even a small percentage of delayed requests can disrupt real-time systems, like financial trading or e-commerce.
In these environments, tail latency can lead to poor user experiences and business consequences. Optimizing data management through better replication can significantly reduce tail latency. A simplified approach to data management ensures that data is more accessible, improving performance. Simplyblock’s approach to simplifying data management directly addresses these issues by ensuring quick and reliable access.
How Replication Helps Minimize Tail Latency
Replication plays a critical role in reducing tail latency by ensuring that data is available across multiple systems or regions. This improves data availability and ensures quicker access to data, thus decreasing tail latency.
Here’s how replication helps reduce tail latency:
- Data Availability: Replication creates multiple copies of data across different servers or regions. This ensures that even if one server experiences high latency, data can be accessed from the nearest available replica, reducing delays.
- Load Balancing: Replication ensures that data is distributed evenly across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck. If one server experiences high load or slowdowns, traffic can be rerouted to another replica, thus reducing tail latency.
- Geographically Distributed Replication: In distributed systems, replicating data across different geographical regions ensures that users can access the nearest data center, minimizing network latency and reducing tail latency.
For instance, implementing cloud-based replication can significantly reduce tail latency. Leading services like AWS and Google Cloud provide replication features to ensure faster access across multiple regions.
Tail Latency vs Average Latency – What’s the Difference?
Understanding the difference between tail latency and average latency is key to managing performance in distributed systems. Below is a table that compares the two:
| Feature | Tail Latency | Average Latency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The slowest requests in a system (e.g., top 1%) | The average time taken for most requests |
| Impact on User Experience | Affects real-time applications and performance | Less noticeable, but still affects performance |
| Causes | Network congestion, overloaded servers, replication lag | General network delays or hardware limits |
| Optimization Focus | Minimized through replication, failover, and load balancing | Improved with better infrastructure and faster networks |
| Real-World Example | Slow trading transactions or delayed video streams | Standard web page load times |
As shown in the table, tail latency can drastically impact the responsiveness of time-sensitive applications, whereas average latency reflects the overall performance of the system.
Best Practices for Minimizing Tail Latency
While replication is crucial for reducing tail latency, there are several other strategies you can implement to further optimize performance:
- Use Edge Computing: By processing data closer to the user, edge computing reduces the distance data travels, thus reducing tail latency.
- Efficient Caching: Store frequently accessed data in memory or fast storage systems to reduce retrieval times and alleviate strain on back-end systems.
- Monitor and Analyze Latency: Continuously track latency issues within your system to identify sources of tail latency and optimize those areas before they impact users.
To further reduce tail latency and optimize your cloud infrastructure, consider exploring Simplyblock’s Cloud Cost Optimization Use Case.
How Simplyblock Helps Reduce Tail Latency
Simplyblock offers robust solutions for reducing tail latency through its built-in data replication and load balancing capabilities. By ensuring data is replicated across multiple regions and data centers, Simplyblock minimizes the risk of tail latency and ensures fast, reliable access to data.
With Simplyblock, you get:
- Real-time data replication across regions to reduce latency
- Advanced failover mechanisms that automatically reroute traffic to low-latency replicas
- Load balancing to ensure even distribution of data and prevent bottlenecks
Simplyblock’s approach ensures that your system remains fast and responsive, even during periods of high demand. For more details on how Simplyblock helps reduce tail latency, you can visit our Database Performance Optimization Use Case.
Strategies for Reducing Tail Latency
Tail latency remains one of the biggest challenges in distributed systems, but with the right strategies in place, it can be minimized. Replication plays a vital role in ensuring data is available from the closest source, but it’s not the only measure. Optimizing your infrastructure, leveraging edge computing, and continuously analyzing your system performance can all help reduce tail latency.
For a comprehensive solution to reducing tail latency and improving overall system performance, consider implementing replication strategies across regions with Simplyblock. Explore our Hybrid Multi-Cloud Storage solutions to help improve data availability and reduce latency across your infrastructure.
Questions and answers
Tail latency plays a critical role in the performance of modern storage systems, as it refers to the delay experienced by the slowest requests. In systems like NVMe over TCP, high tail latency can lead to inconsistent access times, which is detrimental for applications requiring fast, reliable data access. Reducing tail latency is essential to maintaining smooth system performance, especially for high-performance computing and real-time applications.
NVMe over TCP reduces tail latency by optimizing data transfers and reducing protocol overhead, ensuring faster and more consistent performance, even under heavy load. Unlike iSCSI, which may experience unpredictable latency spikes, NVMe over TCP guarantees lower and more stable tail latencies, making it ideal for workloads where latency is crucial, such as cloud storage.
Tail latency is critical for real-time applications such as databases, streaming services, and financial transactions, where delays can lead to significant disruptions. Minimizing tail latency ensures timely data access, preventing slowdowns in high-demand environments. Simplyblock’s storage solutions are designed to optimize latency for such time-sensitive applications.
Tail latency can significantly degrade database performance by increasing the response time of slow queries or transaction processing. Even if the average latency is low, spikes in tail latency can cause bottlenecks in high-demand environments. NVMe over TCP helps eliminate these spikes, ensuring consistent, low latency for faster data processing in database-driven applications.
Yes, tail latency can be minimized in hybrid storage environments by leveraging high-performance protocols like NVMe over TCP alongside strategies such as replication and load balancing. These approaches ensure that even during periods of peak demand, the system can maintain low and stable tail latency, improving overall performance and availability.
