Asynchronous Storage Replication
Terms related to simplyblock
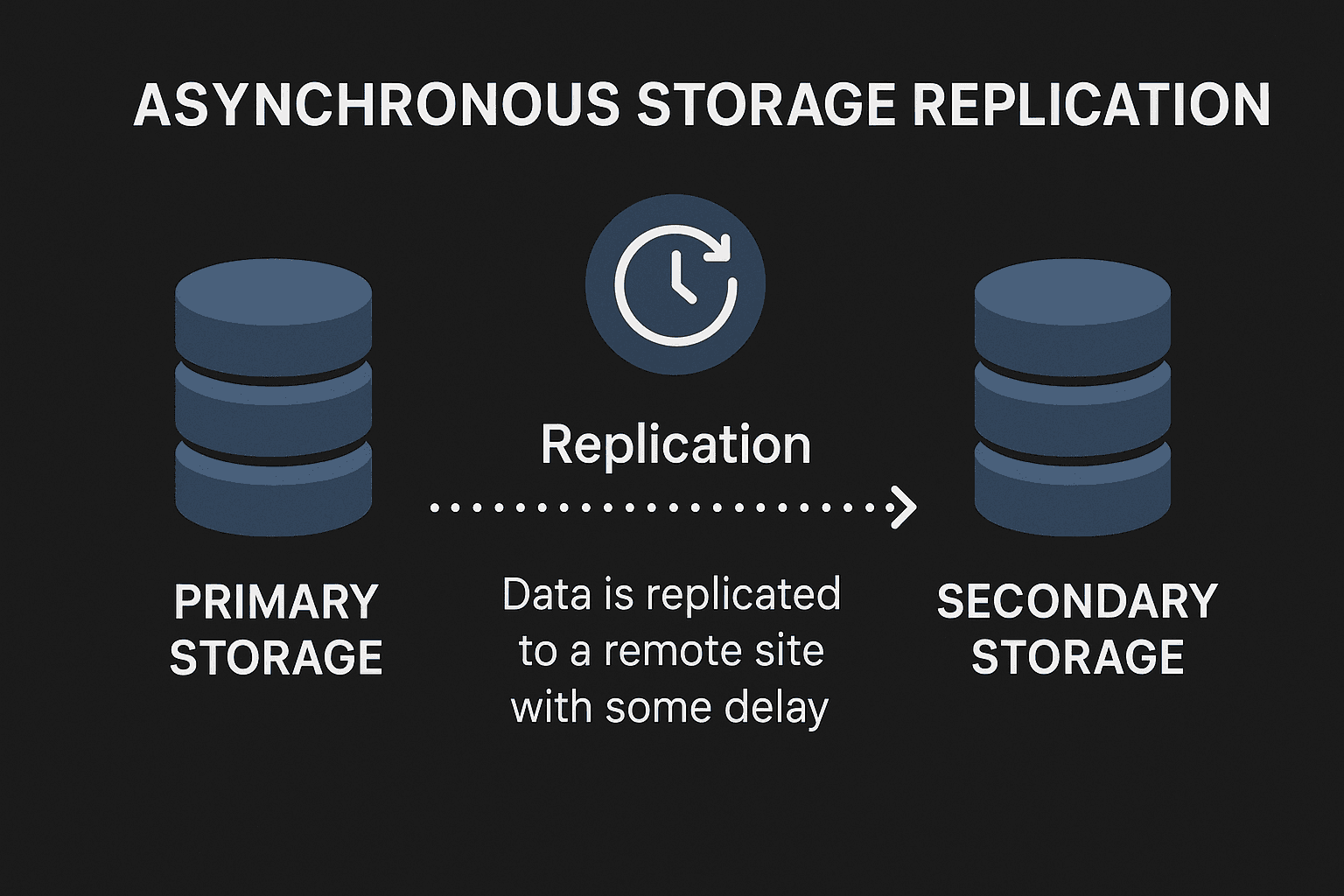
Asynchronous Storage Replication is a data replication strategy designed to provide data protection while minimizing the performance impact on primary systems. Unlike synchronous replication, where data is replicated in real-time, asynchronous replication introduces a slight delay in data mirroring.
This makes it ideal for businesses that need to protect their data across different locations but can tolerate a short delay in data synchronization.
How Asynchronous Replication Storage Operates
Asynchronous Storage Replication works by initially writing data to the primary storage system and then, after a short delay, copying it to the secondary storage system. The replication process doesn’t hold up the primary system, allowing for continuous data access, which is crucial for high-performance environments.
This delay in data synchronization can vary, but typically, the system replicates data in batches at scheduled intervals (e.g., every few seconds or minutes). As a result, asynchronous replication doesn’t affect the performance of the primary system as much as synchronous methods, but it introduces the risk of slight data inconsistency in the event of a failure.
🚀 Optimize Your Storage with Asynchronous Storage Replication
Enhance data protection while maintaining system performance with simplyblock’s advanced Asynchronous Storage Replication solutions.
👉 Learn More About Fast Backups and Disaster Recovery →
Leveraging Asynchronous Replication in Distributed Systems
In distributed environments, where data is spread across multiple geographic locations, Asynchronous Storage Replication plays a critical role in ensuring that data remains protected and available across all locations. Organizations can leverage asynchronous replication to keep a copy of critical data in remote data centers without significant performance overhead.
While it’s not suitable for environments that require real-time data consistency, asynchronous replication offers flexibility and scalability, making it an excellent choice for scenarios where disaster recovery, data backup, and long-distance replication are essential, but near-zero data loss is not critical.
Key Benefits of Asynchronous Storage Replication
Asynchronous Storage Replication offers several key advantages, especially for businesses that need to balance data protection with operational performance:
- Minimal Performance Impact: Since the replication process occurs in the background, asynchronous replication doesn’t negatively affect the performance of the primary storage system during regular operations.
- Cost-Effective for Long-Distance Replication: Asynchronous replication is often more cost-effective for long-distance replication because it minimizes the bandwidth requirements compared to synchronous solutions, which can be more expensive to implement.
- Flexibility: Asynchronous replication allows for flexible replication schedules, such as hourly or daily intervals, which can be adjusted to the needs of the business.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup: This method ensures that a secondary copy of critical data is available in case of a failure, making it an important part of a disaster recovery strategy.
While asynchronous replication doesn’t offer the same level of data consistency as synchronous methods, it provides an ideal solution for businesses that can tolerate a small delay in data replication and prioritize performance over real-time synchronization.
Use Cases for Asynchronous Storage Replication
Asynchronous Storage Replication is widely used in environments where cost-effective, scalable data protection is required, and real-time consistency isn’t a critical need. Some of the common use cases include:
- Disaster Recovery: Many businesses use asynchronous replication as part of their disaster recovery strategy, allowing them to replicate data from their primary data center to a remote location. In case of a failure, the replicated data can be used to restore operations quickly, even though it may not be perfectly up-to-date.
- Backup and Archiving: Asynchronous replication is often used for creating backup copies of important data, enabling organizations to store data in a secondary location without placing a heavy load on their primary systems.
- Cloud Data Replication: In cloud environments, asynchronous replication is commonly used to replicate on-premises data to the cloud or between cloud regions. This allows businesses to maintain a backup of their data in the cloud without disrupting the performance of their on-premise systems.
- Data Distribution: Large-scale businesses that need to distribute data across multiple regions or data centers use asynchronous replication to replicate and maintain copies of data at remote locations without affecting the speed of their primary operations.
Asynchronous Storage Replication vs Synchronous Replication
While asynchronous replication is suitable for many use cases, it’s important to understand how it compares to synchronous replication, which provides real-time data mirroring. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Asynchronous Replication | Synchronous Replication |
| Data Consistency | Risk of data inconsistency in case of failure | Ensures data consistency across all systems |
| Latency | Higher latency, as data is replicated after a delay | Low latency, data is replicated in real-time |
| Data Loss | Risk of data loss if the primary system fails before replication | Zero data loss, all writes are replicated |
| Performance Impact | Minimal impact on the primary system’s performance | Can affect system performance during replication |
| Cost | More cost-effective for long-distance replication | More expensive, especially for long distances |
| Ideal For | Disaster recovery, backups, and remote replication | Mission-critical environments where real-time consistency is required |
How Asynchronous Storage Replication Works in the Cloud
Asynchronous Storage Replication plays a crucial role in cloud-based infrastructures, where data must be replicated across multiple regions to ensure availability and fault tolerance. For example, cloud service providers often use asynchronous replication to synchronize data between their data centers in different locations, ensuring that users have access to their data regardless of regional failures.
This replication method is particularly valuable for cloud disaster recovery strategies, allowing businesses to keep copies of their data in the cloud without overloading their primary systems or incurring high costs associated with synchronous replication.
Streamlining Asynchronous Storage Replication with Simplyblock
Simplyblock helps optimize Asynchronous Storage Replication by providing seamless integration and management for large-scale storage environments. With simplyblock, organizations can:
- Simplify Replication: Easily set up and manage asynchronous replication between multiple storage systems, regardless of the distance between them.
- Ensure Business Continuity: Keep backup copies of data available for disaster recovery and minimize the downtime associated with system failures.
- Improve Performance: Simplyblock ensures that the replication process doesn’t impact the performance of the primary storage system, providing an efficient and effective solution for businesses with high-performance requirements.
- Reduce Complexity: With Simplyblock’s intuitive interface and automated processes, organizations can minimize the complexity of managing asynchronous replication setups across multiple locations, streamlining administration and reducing the likelihood of human error.
Adapting Asynchronous Storage Replication
As data grows, Asynchronous Storage Replication continues to evolve, offering scalable and cost-effective solutions that don’t compromise performance.
With advancements in cloud infrastructure, data analytics, and distributed systems, asynchronous replication will remain a key choice for balancing cost, performance, and data protection across distributed systems.
Related Terms
Teams often review these glossary pages alongside Synchronous Storage Replication when they set write-acknowledgement expectations, validate failure handling, and define recovery and performance targets.
Storage Controller
Storage Pools
Fault Tolerance
SLO (Service Level Objective)
Questions and Answers
Asynchronous storage replication introduces a delay between data changes on the primary storage and their reflection on the secondary storage. While this can lead to temporary data inconsistencies between the sites, it allows for reduced system load and flexibility in data transfer, making it suitable for non-real-time applications.
Asynchronous storage replication is commonly used for disaster recovery, backup systems, and data migration in businesses with less stringent real-time data consistency requirements. It is ideal for applications that can tolerate replication delays, such as large-scale data analytics, file archiving, and off-site backups.
Network latency plays a smaller role in asynchronous storage replication compared to synchronous replication, as data is replicated with a delay. However, high latency can still impact the time taken for data to sync between the primary and secondary storage, potentially delaying disaster recovery or backup completion.
Implementing asynchronous storage replication requires reliable, high-bandwidth network infrastructure between the primary and secondary storage sites. Since the replication occurs with a delay, the network needs to be capable of handling large amounts of data efficiently without overwhelming the system, especially over long distances.
The main risk of asynchronous storage replication is the potential for data loss if a failure occurs at the primary site before replication completes. Additionally, because the replication is delayed, the secondary storage might not have the most current data, which could be problematic during failover or recovery scenarios.
