Scale-Out Block Storage
Terms related to simplyblock
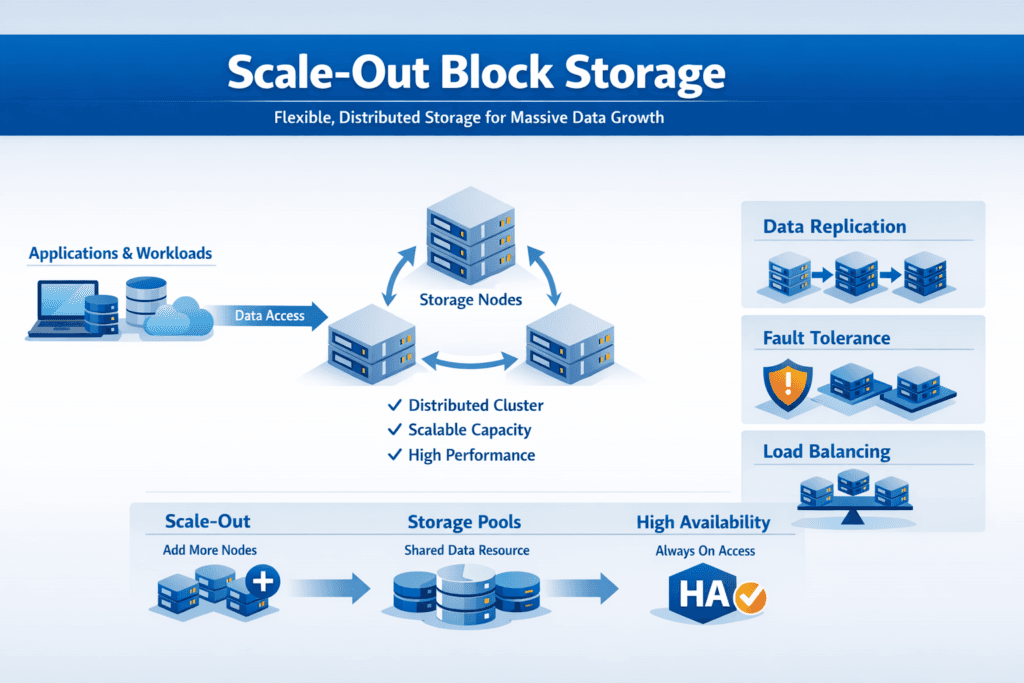
Scale-Out Block Storage is a block storage model that grows by adding more nodes to a storage cluster, instead of upgrading a single controller or array. Each node contributes capacity, performance, or both, and the system spreads data and I/O across the cluster to keep growth predictable. This approach aligns with horizontal scaling concepts used across modern infrastructure.
Executives care about it because it reduces forklift upgrades, limits dependence on proprietary arrays, and supports steady expansion as data and workload demand rise. Platform teams care because it supports automation, workload isolation, and consistent volume behavior across bare metal, virtualization, and cloud environments.
Scale-out designs also pair well with Software-defined Block Storage, because software can manage placement, protection, and performance policies across many nodes while using standard servers and NVMe media.
Scale-Out Design Choices That Reduce Risk
A scale-out system succeeds when it stays simple under change. The core design goal is repeatable operations as nodes join, fail, or get replaced. That means fast rebuild behavior, clear fault domains, and telemetry that helps teams spot hotspots before applications feel them.
Data protection decisions shape both cost and performance. Replication favors simpler failure handling, while erasure coding can improve usable capacity efficiency when configured correctly. Some platforms position erasure coding as a key lever in scale-out architectures to reduce cost per GB without giving up resilience.
To keep performance stable, strong systems avoid uneven placement and reduce “hot” nodes. They rebalance data and load as the cluster grows, so new nodes add real value instead of sitting idle.
🚀 Add Nodes, Not Bottlenecks, with Scale-Out Block Storage on NVMe/TCP
Use Simplyblock to expand capacity and performance linearly, while keeping QoS and tenant isolation in Kubernetes Storage.
👉 See Simplyblock’s Scale-Out Architecture →
Scale-Out Block Storage for Kubernetes Storage
In Kubernetes Storage, scale-out block storage matters because stateful workloads often grow faster than the teams that manage them. A scale-out model supports dynamic provisioning patterns and helps clusters add capacity without redesigning the storage layer. It also fits disaggregated and hyper-converged layouts, so teams can match locality, cost, and scaling needs to each environment.
For multi-tenant clusters, the platform must enforce isolation. Without controls, one noisy workload can push tail latency up for everyone. Scale-out works best when the system supports clear workload boundaries, per-volume limits, and a consistent operational model across dev, staging, and production.
Scale-Out Block Storage with NVMe/TCP Fabrics
NVMe/TCP helps scale-out block storage because it runs over standard Ethernet and TCP/IP, which makes rollouts easier across mixed data centers. It supports a practical disaggregation model, where compute and storage scale on their own timelines, while still keeping NVMe semantics for efficient I/O.
NVMe/TCP can cost more CPU than RDMA-based options, so the storage stack and datapath efficiency matter. Teams often win by keeping the I/O path lean, pinning hot threads, and using a storage engine designed for NVMe-class queues. Those steps help keep latency steady as concurrency rises.
Benchmarking Scale-Out Block Storage Under Real Load
Scale-out performance discussions break down when teams rely on peak numbers from one node or one short test. A useful plan measures outcomes across node counts and keeps the workload shape consistent. Track IOPS, throughput, and tail latency, then relate each result to CPU use per node.
Tail latency deserves special focus because applications feel the slow outliers, not the average. Kubernetes adds more variability through shared networking, scheduling, and noisy-neighbor effects, so tests should include multi-tenant pressure and background activity when possible.
A practical benchmark method also checks scaling behavior. If you add nodes and performance stays flat, something blocks parallelism. That “something” is often networking, placement imbalance, or an inefficient data path.
Practical Tuning for Lower Latency and Better Scale
Most improvements come from reducing variance and enforcing isolation. Use this checklist as a starting point:
- Keep the data path efficient by cutting extra copies and avoiding unnecessary kernel overhead when the platform supports it.
- Apply QoS limits and tenant boundaries so one workload cannot dominate queues.
- Validate the network path first, including MTU consistency and congestion behavior, before changing storage settings.
- Use repeatable fio profiles and gate changes on p95 and p99 latency, not just average throughput.
- Confirm that rebalancing and rebuilding traffic cannot starve foreground I/O during node changes.
Comparing Scale-Out Block Storage Models
The table below compares common approaches, with emphasis on how they behave as data and workload demand grow.
| Attribute | Scale-Up Array (Traditional) | Cloud Managed Volumes | Scale-Out Block Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth method | Bigger controller or shelf | Provider limits and tiers | Add nodes to a cluster |
| Failure handling | Controller-centric | Provider-managed | Distributed across nodes |
| Kubernetes fit | Often bolted on | Cloud-specific | Designed for cluster growth |
| Performance scaling | Peaks early | Varies by tier | Grows with node count (when balanced) |
| Cost behavior | Forklift cycles | OPEX can spike | Incremental expansion |
| Typical role | Legacy SAN footprint | Single-cloud ops | Hybrid, bare metal, and cloud-native |
Scale-Out Block Storage with Simplyblock™
Simplyblock™ positions its platform as NVMe-first and Kubernetes-focused, using NVMe/TCP and an architecture built for scale-out behavior. It targets performance efficiency with an SPDK-accelerated, user-space style datapath, which helps reduce CPU waste and supports steadier latency under load.
Simplyblock™ also supports flexible deployment patterns, including disaggregated and hyper-converged layouts, so teams can choose the right fit per cluster. For multi-tenant environments, the value comes from workload isolation and QoS controls that keep business-critical services protected when the platform gets busy.
Where Scale-Out Architectures Go Next
Scale-out storage keeps moving toward tighter control loops and better automation. Expect more policy-driven placement, smarter rebuild scheduling, and faster rebalancing that avoids foreground disruption. Hardware offload via DPUs or IPUs will also matter more as NVMe speeds rise and CPU cycles become a tighter budget across large clusters.
At the platform layer, tighter integration with Kubernetes scheduling and topology signals should make “right volume, right node, right tier” a standard outcome, not a manual process.
Related Terms
Teams often review these glossary pages with Scale-Out Block Storage when they design Kubernetes Storage on NVMe/TCP.
Questions and Answers
Scale-out block storage distributes data and I/O across multiple nodes, allowing linear performance and capacity scaling. It eliminates bottlenecks found in monolithic storage systems, making it ideal for Kubernetes workloads and cloud-native environments that require high availability and throughput.
Traditional SANs are centralized and often tied to specific hardware, limiting scalability. In contrast, scale-out block storage uses a distributed architecture and commodity hardware, allowing you to add storage nodes independently. This model supports elastic growth and fault tolerance.
Yes, NVMe over TCP is ideal for scale-out block storage. It allows each node in a cluster to provide high-performance NVMe-backed volumes over standard Ethernet, enabling low-latency storage that scales without specialized networking gear.
Scale-out block storage supports high-growth workloads like distributed databases, analytics platforms, and containerized applications. It’s also a strong fit for multi-tenant Kubernetes clusters needing scalable, isolated, and resilient persistent storage.
Simplyblock provides a software-defined, scale-out block storage solution using NVMe over TCP. It supports instant snapshots, per-volume encryption, and replication across nodes—delivering high performance and flexibility in Kubernetes and VM environments.
