SAN Replacement with NVMe over TCP
Terms related to simplyblock
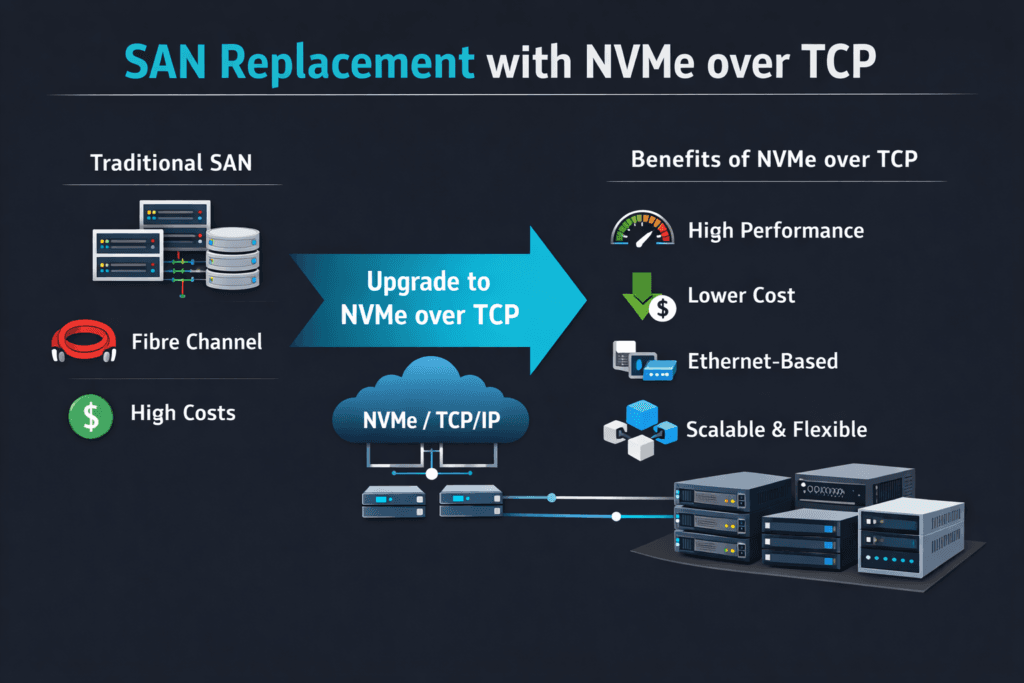
SAN Replacement with NVMe over TCP means shifting from a classic SAN model to NVMe/TCP over standard Ethernet, backed by scale-out Software-defined Block Storage. Teams make this move to cut latency, raise IOPS, and avoid the cost curve of proprietary controllers and expansion shelves.
This change also resets how storage teams work. A SAN often relies on tickets, manual zoning, and LUN workflows. A SAN replacement that fits Kubernetes Storage favors self-service, policy, and fast change cycles, while still keeping guardrails for risk and uptime.
Designing a Faster SAN Alternative with User-Space NVMe-oF
A fast SAN alternative starts with the IO path. NVMe/TCP performs best when the platform keeps copies, interrupts, and context switches low. User-space designs that use SPDK help by pushing more work through a tight, efficient path and keeping CPU per IO under control.
Modern systems also bring controls you can measure. You can set limits, track hot volumes, and enforce priorities. Those knobs matter in shared environments where a single app can spike queue depth and push up tail latency for everything else.
🚀 Replace Fibre Channel SAN with NVMe/TCP, Natively in Kubernetes
Use Simplyblock to migrate to Software-defined Block Storage, cap latency spikes, and scale out on Ethernet.
👉 Use Simplyblock for NVMe over TCP Storage →
SAN Replacement with NVMe over TCP in Kubernetes Storage
Kubernetes Storage changes the definition of “enterprise-ready.” Storage must provision fast, attach cleanly, and recover without long maintenance windows. Manual SAN steps slow teams down, especially when clusters scale and apps roll out often.
NVMe/TCP fits Kubernetes Storage because it runs on routable IP networks and common Ethernet. With Software-defined Block Storage, you can map storage classes to tiers, then let CSI handle create, expand, and attach operations. That approach links storage changes to the same workflow teams already use for apps.
SAN Replacement with NVMe over TCP and NVMe/TCP Network Design
NVMe/TCP carries NVMe commands over TCP/IP, so it works with standard switches and common tooling. That makes adoption easier than fabric-heavy options, while still supporting high parallel IO.
For SAN replacement, focus on two things: tail latency and fairness. Tail latency drives timeouts and retries, which then amplify load. Fairness keeps one host from drowning out others. A good NVMe/TCP design keeps queues stable, avoids CPU hotspots, and protects p99 latency during bursts.
Measuring SAN Replacement with NVMe over TCP Performance
Benchmarks should match how your apps behave. Use small-block random IO for databases, steady writes for logs, and large reads for analytics. Run tests with real concurrency because quiet tests hide noisy-neighbor risk.
Track results across runs, not just one “best” run. Watch p95 and p99 latency, IOPS at a fixed latency target, throughput under peak load, and CPU per IO. A SAN replacement succeeds when performance stays steady as you add nodes, add tenants, and grow capacity.
Tuning Steps to Cut Latency Spikes During Migration
Most performance issues come from a small set of causes. Fix them early, and the rollout moves faster.
- Split storage classes into tiers, and set clear caps for IOPS and throughput per tier.
- Keep NVMe/TCP settings consistent across nodes, including MTU, IRQ placement, and CPU pinning.
- Watch queue depth and percentiles, then tune for p99 instead of averages.
- Put batch jobs in capped tiers so bursts do not crush OLTP workloads.
- Scale out before saturation, then re-run the same test profile after each change.
Storage Architectures Compared for SAN Modernization
The table below summarizes the trade-offs teams often see when they compare SAN paths to Ethernet NVMe options. Use it to frame both cost and risk, not just raw speed.
| Approach | Typical wins | Typical limits | Best fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keep legacy SAN | Familiar process, stable baseline | Controller bottlenecks, high expansion cost | Stable legacy estates |
| iSCSI refresh | Easy to roll out | Higher overhead than NVMe/TCP | Mid-range workloads |
| NVMe/TCP on Software-defined Block Storage | Scale-out growth on Ethernet, strong parallel IO | Needs strong QoS and clean tuning | Kubernetes-first platforms |
| NVMe/RDMA fabrics | Strong tail latency potential | Fabric complexity, strict ops needs | Tightest latency tiers |
SAN Replacement with NVMe over TCP with Simplyblock™
Simplyblock™ supports SAN replacement goals with an SPDK-based, user-space data path and policy controls that fit Kubernetes Storage. This design helps keep CPU cost low and latency stable as IO rises. It also supports flexible layouts, including hyper-converged, disaggregated, and mixed deployments.
Simplyblock™ supports NVMe/TCP and NVMe/RoCEv2, so teams can use standard Ethernet for broad adoption and reserve RDMA tiers for the strictest targets. Multi-tenancy and QoS let platform teams set clear limits, protect high-priority apps, and reduce noisy-neighbor risk on shared Software-defined Block Storage.
Next Steps for Ethernet NVMe and SAN Alternatives
SAN replacements keep moving toward a platform model. Teams want clear tiers, clear targets, and repeatable tests tied to real app behavior. Expect more user-space acceleration, more automation, and more policy close to the IO path.
DPUs and IPUs will also help as orgs offload parts of the storage path and free host CPU for workloads.
Related Terms
These glossary pages support SAN replacement planning when teams standardize Kubernetes Storage and Software-defined Block Storage.
Questions and Answers
NVMe over TCP delivers similar or better performance than traditional SANs while using standard Ethernet instead of proprietary Fibre Channel. It reduces latency, increases IOPS, and scales horizontally, making it a strong candidate to replace legacy SAN systems.
Replacing SAN with NVMe over TCP eliminates expensive, specialized hardware and simplifies networking with TCP/IP. Combined with a software-defined block storage platform like Simplyblock, you gain scalability, agility, and modern automation features.
Compared to iSCSI, NVMe over TCP offers significantly lower latency and up to 35% higher IOPS. It supports high-performance storage over standard Ethernet networks, making it ideal for modern SAN replacements. See our detailed NVMe over TCP vs iSCSI comparison.
Yes, modern platforms like Simplyblock provide NVMe over TCP with enterprise-grade features such as synchronous replication, snapshots, and encryption. This ensures a seamless transition from legacy SAN to next-gen distributed storage.
Migration is simplified with platforms that support both SAN protocols and NVMe over TCP. Simplyblock allows provisioning of iSCSI and NVMe volumes side-by-side, enabling phased migration without downtime or rearchitecture.
