NVIDIA BlueField DPU
Terms related to simplyblock
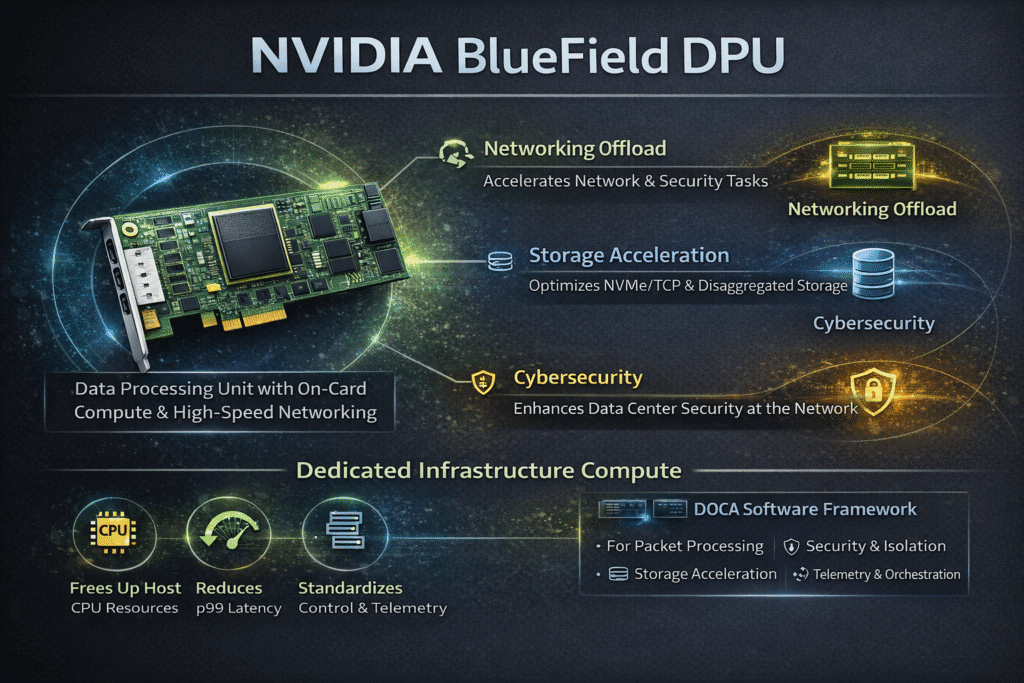
An NVIDIA BlueField DPU is designed to handle infrastructure work that usually overloads host CPUs. By combining high-speed networking with on-card compute, it runs packet processing, security, and storage-related tasks closer to the network.
NVIDIA positions BlueField as an infrastructure compute platform for networking, storage, and cybersecurity. In Kubernetes Storage environments, this approach helps reduce CPU contention, keep latency stable, and maintain consistent performance under heavy I/O load.
Why Data Centers Use NVIDIA BlueField DPU for Offload
Platform teams adopt a DPU when host CPUs spend too much time on network and security work. East-west traffic grows, encryption becomes the default, and policy checks add overhead. Those costs hit hardest when you run high-throughput storage, and you also want tight isolation.
BlueField helps you shift key data-path tasks off the host, which can improve CPU headroom and stabilize p99 latency. NVIDIA’s DPU overview frames this as a move from CPU-only infrastructure to dedicated infrastructure compute.
🚀 Put NVIDIA BlueField DPU Offload to Work
See how DPU acceleration supports NVMe/TCP and Kubernetes Storage, then map it to your cluster design.
👉 See DPU Acceleration for NVMe/TCP →
NVIDIA BlueField DPU and the DOCA Software Stack
NVIDIA builds BlueField around DOCA, which provides a common software layer for writing, packaging, and operating DPU services. In practice, DOCA lets platform teams treat the DPU as a standardized infrastructure runtime for data path functions like packet steering, security policy enforcement, and telemetry, instead of relying on host-side agents that compete for CPU.
DOCA also helps with fleet operations. Teams can keep the same service logic across different servers, roll updates in a controlled way, and enforce consistent security and networking behavior across environments. That consistency matters in large Kubernetes Storage footprints, where drift in node-level networking and security settings can translate into unstable p99 latency and noisy-neighbor incidents.
Using NVIDIA BlueField DPU in NVMe/TCP Storage Networks
NVMe/TCP runs NVMe commands over standard Ethernet and TCP/IP, which makes it practical for disaggregated designs and SAN alternative builds. At high IOPS, the host still pays for packet work, policy checks, and telemetry. When you stack encryption and multi-tenant controls, that overhead can squeeze the CPU budget that applications need.
A BlueField DPU can move parts of that work closer to the wire, which helps preserve host CPU headroom for storage engines and application threads. This matters most in shared Kubernetes clusters where one busy tenant can trigger CPU contention and push tail latency out of SLO.
Kubernetes Storage Architectures That Benefit from DPUs
In Kubernetes Storage, a DPU does not replace your storage platform. It supports the network and security layer that storage depends on. You still need Software-defined Block Storage to provide block semantics, resiliency, snapshots, multi-tenancy, and QoS.
Hyper-converged clusters run compute and storage on the same nodes, so CPU contention shows up quickly. Disaggregated clusters separate storage nodes from app nodes, so the network path becomes the performance focus. BlueField can help in both models by keeping infrastructure work away from host CPUs.
Performance and CPU Efficiency in Software-Defined Block Storage
DPU offload works best when the rest of the data path stays lean. Many storage teams target user-space I/O paths and fewer data copies to reduce jitter. That approach helps keep p99 stable while you raise throughput.
Simplyblock focuses on Software-defined Block Storage for Kubernetes Storage with NVMe/TCP support, which fits this model when you need high performance on standard Ethernet.
Comparison of infrastructure offload options for Kubernetes Storage
The table below shows where each option runs key infrastructure work and how that choice tends to affect storage-heavy clusters.
| Option | Where infrastructure work runs | Typical impact on Kubernetes Storage |
| CPU-only | Host CPU and kernel | More CPU contention during traffic spikes, higher tail-latency risk |
| SmartNIC | NIC offload for select functions | Helps specific tasks, leaves more platform work on the host |
| NVIDIA BlueField DPU | On-card compute plus high-speed networking | Frees host CPU for apps and storage, steadier p99 under load |
| IPU | Dedicated infrastructure complex | Strong isolation between apps and platform services |
Simplyblock™ with NVIDIA BlueField DPU for NVMe/TCP Kubernetes Storage
Simplyblock pairs naturally with DPU-first infrastructure because both focus on keeping overhead out of the application path. Simplyblock delivers Software-defined Block Storage for Kubernetes Storage over NVMe/TCP, with multi-tenancy and QoS controls.
Teams that evaluate BlueField often track two numbers: host CPU use during peak I/O and p99 latency during noisy-neighbor events. When those metrics improve, DPUs and storage policy controls start paying for themselves.
Related Technologies
These glossary terms are commonly reviewed alongside NVIDIA BlueField DPU when planning offload-heavy networking and storage data paths in Kubernetes Storage.
PCI Express (PCIe)
RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access)
NVMe/RDMA
DPDK (Data Plane Development Kit)
Observability
Questions and Answers
NVIDIA BlueField offloads storage, networking, and security functions from the host CPU, enabling efficient data processing at the edge. It’s used for tasks like NVMe-oF target offload, vSwitch acceleration, and TLS termination—all on the DPU itself.
BlueField DPUs handle NVMe over Fabrics at the hardware level, allowing NVMe/TCP targets to run directly on the DPU. This boosts throughput, cuts latency, and eliminates the need for CPU-based storage management in disaggregated architectures.
Yes, unlike basic SmartNICs, BlueField DPUs run full Linux OS instances and support advanced offloads for storage, security, and networking. This makes them ideal for running services like software-defined storage or virtual switches in cloud-native stacks.
Absolutely. BlueField offloads networking (e.g., vSwitch), encryption, and storage I/O, freeing CPU for application workloads. This enhances pod density, reduces latency, and simplifies Kubernetes storage provisioning.
BlueField enables hardware-level isolation for networking and storage by enforcing policies on the DPU itself. This reduces attack surfaces and supports secure multi-tenant Kubernetes or VM-based architectures.
