Disaggregated Storage
Terms related to simplyblock
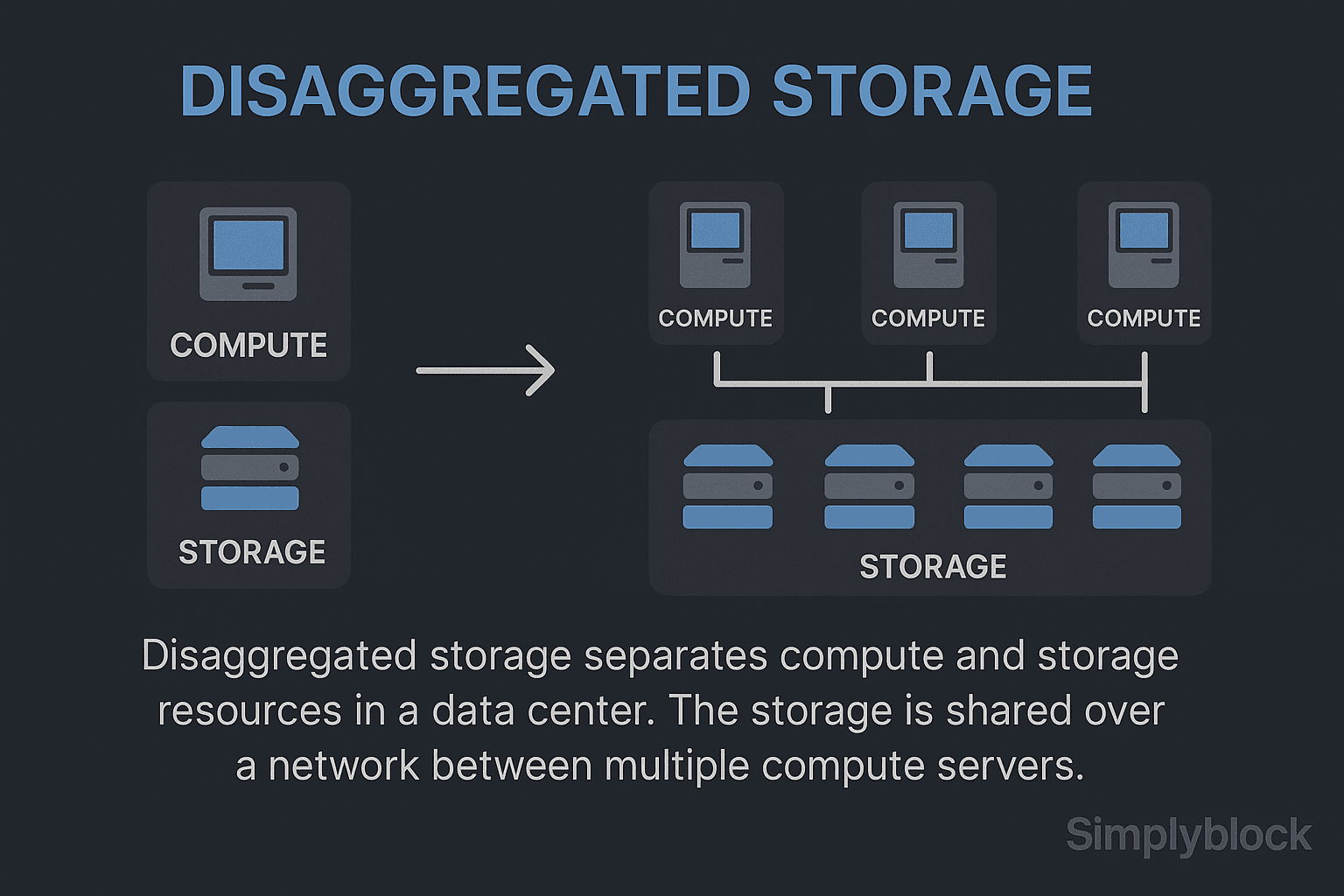
Disaggregated storage is a modern architecture that separates compute resources from storage resources across a network, instead of combining them within the same server or node. This separation enables independent scaling, centralized management, and better resource utilization—making it a preferred model for cloud-native applications, Kubernetes, and software-defined storage platforms like simplyblock.
Unlike traditional hyper-converg
ed infrastructure (HCI), where compute and storage scale together, disaggregated storage allows enterprises to grow storage capacity without provisioning unnecessary CPU or memory, reducing both CapEx and OpEx.
How Disaggregated Storage Works
In a disaggregated system, storage devices (typically NVMe SSDs) are pooled and exposed over a high-speed network fabric such as NVMe over TCP. Compute nodes access storage volumes remotely, while a control plane orchestrates provisioning, replication, and performance policies.
Disaggregated environments often use erasure coding for data protection, enabling efficient fault tolerance without full data replication. The platform may include QoS enforcement, volume snapshots, and dynamic tiering to meet workload-specific SLAs.
Disaggregated vs Hyper-Converged vs Traditional Storage
To better understand where disaggregated storage fits, here’s how it compares to other architectures:
| Feature | Disaggregated Storage | Hyper-Converged | Traditional SAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compute & Storage Coupling | Decoupled | Tightly coupled | Centralized controllers |
| Scalability | Independent for each layer | Must scale in lockstep | Often limited to controller |
| Performance Flexibility | Tuned per workload | Shared CPU/storage bus | High but hardware-bound |
| Fault Tolerance | Cluster-aware, adaptive | Node-level failover | Dual controller failover |
| Suitable for Kubernetes | Yes | Partial support | Complex integration |
| Cost Efficiency | High (no overprovisioning) | Moderate | Expensive upfront hardware |
If you want to learn more about choice right storage in context of Kubernetes, read our blog post on disaggregated and hyper-converged storage for Kubernetes.
Benefits of Disaggregated Storage
Adopting disaggregated storage gains flexibility and performance without sacrificing control:
- Independent scaling: Storage and compute grow at their own pace.
- Higher utilization: No stranded capacity within nodes.
- Cloud-native compatibility: Ideal for Kubernetes persistent volumes and microservices.
- Edge and hybrid readiness: Works across hybrid and air-gapped environments.
- High IOPS, low latency: When paired with NVMe over Fabrics and advanced erasure coding.
Use Cases for Disaggregated Storage
Disaggregated architectures are being adopted across verticals where storage needs grow faster or differently than compute:
- AI/ML Pipelines: Storage-heavy, GPU-dense environments benefit from disaggregated design.
- Big Data Analytics: Systems like Presto, Spark, or ClickHouse demand parallel access to shared high-performance storage.
- Service Providers: Multi-tenant environments with variable storage IOPS and capacity profiles.
- Kubernetes Clusters: Stateless compute layers accessing block volumes via CSI.
- Edge & Telco Infrastructure: Resource isolation across geographies with centralized control.
Disaggregated Storage in Simplyblock
Simplyblock is architected around disaggregated principles. By decoupling compute from storage, it enables:
- Kubernetes-native block storage via CSI
- Storage IOPS scaling independently from application nodes
- Consistent low-latency access using NVMe/TCP
- Cluster-wide snapshots, QoS policies, and adaptive failure domains
This architecture powers everything from cloud database deployments to cost-optimized AWS setups, enabling truly elastic infrastructure.
Related Terms
Teams often review these glossary pages alongside Disaggregated Storage when they separate compute and storage pools, set network-latency budgets, and choose an NVMe-oF transport for Kubernetes Storage running on Software-defined Block Storage.
Network Storage Performance
Block Storage CSI
NVMe-oF (NVMe over Fabrics)
NVMe-oF Target on DPU
External Resources
- Disaggregated Storage Explained – GigaOm
- NVMe over Fabrics – NVM Express
- Open Compute Project: Disaggregated Network
- Erasure Coding – Wikipedia
- CSI Architecture – Kubernetes Documentation
Questions and Answers
Disaggregated storage enables independent scaling of compute and storage, which is critical for cloud-native and Kubernetes environments. It reduces hardware waste, improves flexibility, and supports high-performance workloads by decoupling local storage dependencies.
Unlike DAS or traditional SAN setups, disaggregated storage enables dynamic scaling, better resource utilization, and easier automation. Paired with software-defined storage, it’s ideal for modern cloud-native and Kubernetes environments.
Yes, disaggregated storage aligns perfectly with containerized architectures. Using Kubernetes-native NVMe storage enables persistent, high-performance volumes that can be dynamically provisioned across distributed nodes.
Most modern disaggregated storage platforms support encryption at rest via volume-level security. This is essential for securing data in multi-tenant or regulated environments without compromising performance or scalability.
Disaggregated storage improves performance, lowers total cost of ownership, and simplifies infrastructure scaling. It reduces data silos and supports faster recovery and provisioning, making it ideal for databases, analytics, and Kubernetes-based microservices.
