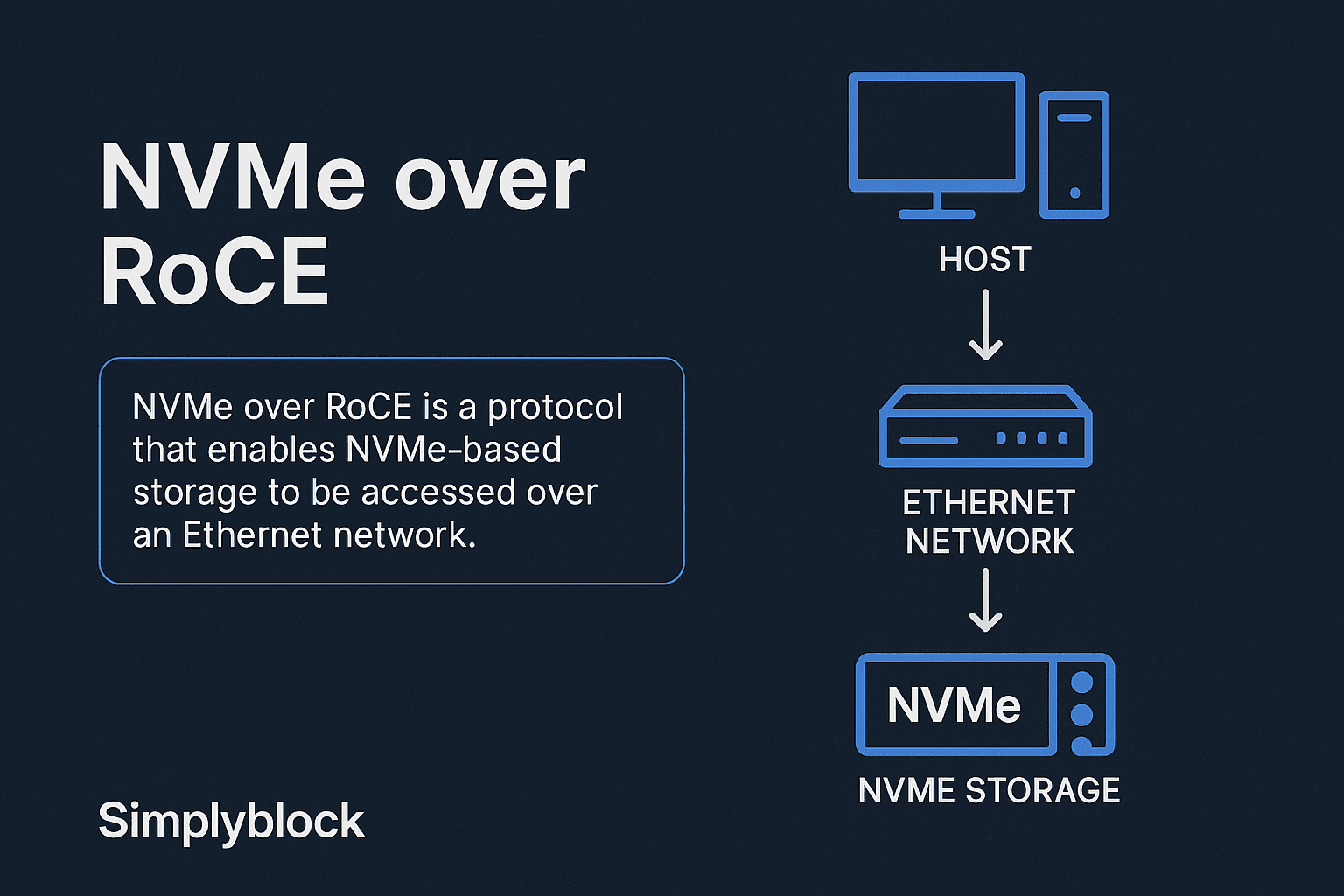
NVMe over RoCE
Terms related to simplyblock
NVMe over RoCE (Remote Direct Memory Access over Converged Ethernet) is a transport protocol under the NVMe over Fabrics family. It allows NVMe commands to be transmitted over high-speed Ethernet via RDMA, enabling extremely low latency and high throughput.
By bypassing the traditional TCP/IP stack and leveraging direct memory access, NVMe over RoCE achieves near-local performance over Ethernet. This makes it highly effective for use cases that demand maximum storage IOPS and minimal latency.
How NVMe over RoCE Works
In an NVMe/RoCE deployment, NVMe commands are encapsulated within RDMA messages transmitted across Ethernet networks. RoCE operates at Layer 2 or Layer 3, depending on whether it’s RoCE v1 or v2. Both versions require a lossless network fabric, typically achieved through Data Center Bridging (DCB) and Priority Flow Control (PFC).
This architecture minimizes CPU utilization by offloading data movement to RDMA-enabled NICs, enabling efficient parallel access to remote NVMe storage targets. To better understand how this differs from TCP-based approaches, review our NVMe over TCP vs iSCSI benchmark.
Benefits of NVMe over RoCE
Key advantages of NVMe/RoCE for high-performance environments include:
- Microsecond latency: Ideal for real-time applications and fast storage access.
- Maximum throughput: Leverages NVMe’s multi-queue parallelism over fast 25/50/100/200 GbE.
- Offloaded processing: Frees up host CPU cycles by offloading transfers to the NIC.
- Optimized for flash: Works best in environments using high-speed NVMe SSDs.
- Supports disaggregated storage: Integrates with modular, adaptive storage architectures like those used by simplyblock.
NVMe over RoCE vs Other Fabrics
While NVMe/RoCE is the lowest-latency NVMe-oF transport, it has stricter infrastructure requirements. For organizations needing simpler deployment and better compatibility, NVMe over TCP is often a better fit.
| Feature | NVMe over RoCE | NVMe over TCP | NVMe over FC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport Medium | RDMA over Ethernet | TCP/IP over Ethernet | Fibre Channel |
| Hardware Requirements | RDMA-capable NICs | Standard NICs | FC HBAs and switches |
| Latency | <100µs | ~300–400µs | ~100–300µs |
| Network Loss Handling | Requires lossless fabric | Tolerant of packet loss | Inherent reliability |
| Scalability | High with careful tuning | High, simple to deploy | Moderate |
| Operational Complexity | High | Low | Moderate |
For detailed comparison of NVMe/TCP vs NVMe/RoCE (NVMe/RDMA) read our blog post on this topic.
Use Cases for NVMe over RoCE
Industries using NVMe over RoCE include:
- AI/ML workloads requiring extreme throughput and parallelism
- Financial trading platforms where latency affects transaction outcomes
- Real-time video analytics and telemetry
- Tier-0 storage in HPC or disaggregated storage environments
- Edge computing nodes with specialized RDMA support
These workloads often also benefit from erasure-coded storage for space-efficient fault tolerance.
NVMe over RoCE and Simplyblock
At simplyblock, the focus is on high-performance NVMe storage over TCP, optimized for Kubernetes, hybrid cloud, and edge deployments.
Our software-defined storage platform delivers sub-millisecond latency without requiring RDMA-capable hardware, allowing broader compatibility and lower total cost of ownership. Features like multi-tenancy with QoS and copy-on-write snapshots make simplyblock suitable for dynamic, container-native environments.
Related Terms
Teams often review these glossary pages alongside NVMe over RoCE when they’re building a stable RDMA fabric on Ethernet, including routing choices, congestion controls, and end-to-end latency budgets.
RoCEv2
RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access)
NVMe/RDMA
InfiniBand
External Resources
- Remote Direct Memory Access – Wikipedia
- RoCE Overview – NVIDIA
- NVMe over Fabrics Spec – NVM Express
- Broadcom RoCE & NVMe Config Guide
Questions and Answers
NVMe over RoCE enables ultra-low latency and high-throughput storage access using RDMA over Ethernet. It’s ideal for data-intensive workloads like high-frequency trading, AI/ML pipelines, and databases that require near-real-time performance on dedicated, lossless networks.
NVMe/RoCE delivers slightly better latency and CPU efficiency than NVMe over TCP, but it requires RDMA-capable NICs and a lossless Ethernet fabric. NVMe/TCP is more flexible, easier to manage, and better suited for Kubernetes and cloud-native workloads.
Technically yes, but RoCE is complex to configure and maintain in dynamic environments like Kubernetes. Kubernetes-native NVMe storage over TCP offers a more operationally friendly alternative for scalable and persistent storage.
The NVMe/RoCE protocol does not include encryption. To ensure secure deployments, especially in multi-tenant or regulated environments, encryption at rest should be implemented at the volume level with per-tenant key isolation.
NVMe/RoCE provides excellent performance but requires specialized hardware, strict networking configurations, and lossless Ethernet. It’s less portable and cloud-native than software-defined storage options that use NVMe/TCP for broader compatibility.
